Accounting is the backbone of every business. Without proper accounting, financial chaos is inevitable. But what ensures that accounting remains standardized, accurate, and trustworthy? The answer lies in accounting principles—a set of guidelines that dictate how financial transactions are recorded and reported.
In this guide, we’ll break down the key accounting principles, why they matter, and how they impact businesses worldwide.
What Are Accounting Principles?
Accounting principles are a set of standardized rules that govern financial accounting practices. They ensure that financial information is accurate, comparable, and transparent. These principles help businesses, investors, and regulators interpret financial statements consistently.
There are two widely accepted accounting frameworks:
- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) – Used mainly in the U.S.
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) – Used in over 140 countries
Both frameworks share common principles, but GAAP tends to be more rule-based, while IFRS is principle-based.
Why Are Accounting Principles Important?
Accounting principles are crucial for several reasons:
- Consistency: Ensures that businesses follow the same accounting methods.
- Comparability: Makes financial statements easy to compare across companies.
- Transparency: Reduces fraud and misrepresentation in financial reporting.
- Decision-Making: Helps investors and stakeholders make informed choices.
Without accounting principles, financial chaos and misinformation would dominate the business world.
Key Accounting Principles You Should Know
Let’s explore the most essential accounting principles that guide financial reporting.
1. Accrual Principle
The accrual principle states that transactions should be recorded when they occur, not when cash is exchanged. This principle distinguishes between cash and accrual accounting, with the latter being the preferred method for most businesses.
Example: A company provides services in December but receives payment in January. Under accrual accounting, the revenue is recorded in December, when the service was performed.
2. Consistency Principle
This principle requires companies to use the same accounting methods and procedures over time. If a company changes its accounting method, it must disclose the change and explain why it’s necessary.
Why It Matters: Ensures comparability of financial statements across different periods.
3. Going Concern Principle
The going concern principle assumes that a business will continue to operate in the foreseeable future. If a company is likely to go bankrupt or shut down, it must disclose this in its financial statements.
Impact: Helps investors assess the long-term viability of a company.
4. Matching Principle
The matching principle ensures that expenses are recorded in the same period as the revenues they help generate. This is fundamental to accrual accounting.
Example: A company pays for advertising in November, leading to increased sales in December. The expense should be recorded in December to match the revenue it generated.
5. Cost Principle
This principle states that assets should be recorded at their original purchase price (historical cost), rather than their current market value.
Limitations: While this ensures reliability, it does not always reflect true asset values due to market fluctuations.
6. Full Disclosure Principle
Financial statements must provide all relevant information that could influence users’ decisions. This includes footnotes, contingent liabilities, and significant financial events.
Why It’s Important: Protects investors and prevents misleading financial reporting.
7. Revenue Recognition Principle
The revenue recognition principle states that revenue should be recorded when it is earned, regardless of when cash is received.
Example: A subscription service recognizes revenue monthly as services are provided, even if the customer paid for the entire year upfront.
8. Objectivity Principle
Financial statements should be based on verifiable and unbiased evidence, not personal opinions or estimates.
Example: If a company buys a machine, its cost should be backed by an invoice or receipt.
9. Conservatism Principle
When faced with uncertainty, accountants should choose the option that least overstates assets and income. This ensures that potential losses are accounted for but not anticipated gains.
Example: If a company expects a potential lawsuit loss, it should record the liability even if the outcome is uncertain.
10. Materiality Principle
This principle states that only significant financial transactions should be recorded. Minor transactions that do not impact decision-making can be ignored.
Example: A company purchasing office supplies worth $20 does not need to record it as a long-term asset.
Also Read : Accounting Policies: Definition, Importance & Key Examples
GAAP vs. IFRS: Key Differences
Although both GAAP and IFRS aim for transparency and accuracy, there are key differences:
| Feature | GAAP (U.S.) | IFRS (International) |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Rule-based | Principle-based |
| Inventory Valuation | Allows LIFO and FIFO | Prohibits LIFO, only FIFO |
| Revenue Recognition | More detailed rules | More flexible principles |
| Development Costs | Expensed immediately | Can be capitalized |
How Accounting Principles Impact Businesses
Accounting principles influence every financial decision in a company. They affect:
- Financial reporting – Ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Taxation – Determining taxable income.
- Investor confidence – Providing reliable data for decision-making.
- Loan approvals – Helping banks assess creditworthiness.
A company’s adherence to accounting principles can mean the difference between financial stability and regulatory trouble.
Conclusion
Accounting principles are the foundation of financial reporting. They ensure that businesses present accurate, transparent, and comparable financial data. Whether you’re an accountant, business owner, or investor, understanding these principles is essential for making informed financial decisions.
By adhering to GAAP or IFRS, companies build trust, maintain compliance, and support economic growth.
lso Read : What is an Accounting Method? Types, Examples, and Best Practices
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the most important accounting principle?
All principles are important, but accrual accounting, consistency, and revenue recognition are fundamental for accurate financial reporting.
2. Why do different countries have different accounting principles?
Each country has its own regulations, economic systems, and legal frameworks, leading to different accounting standards like GAAP (U.S.) and IFRS (international).
3. Can a company switch from GAAP to IFRS?
Yes, but the transition can be complex and requires adjustments to financial statements. Some multinational companies use both standards.
4. How do accounting principles prevent fraud?
By enforcing consistency, transparency, and objectivity, these principles make it harder for companies to manipulate financial data.
5. Where can I learn more about accounting principles?
You can explore resources from the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) for GAAP or the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) for IFRS.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
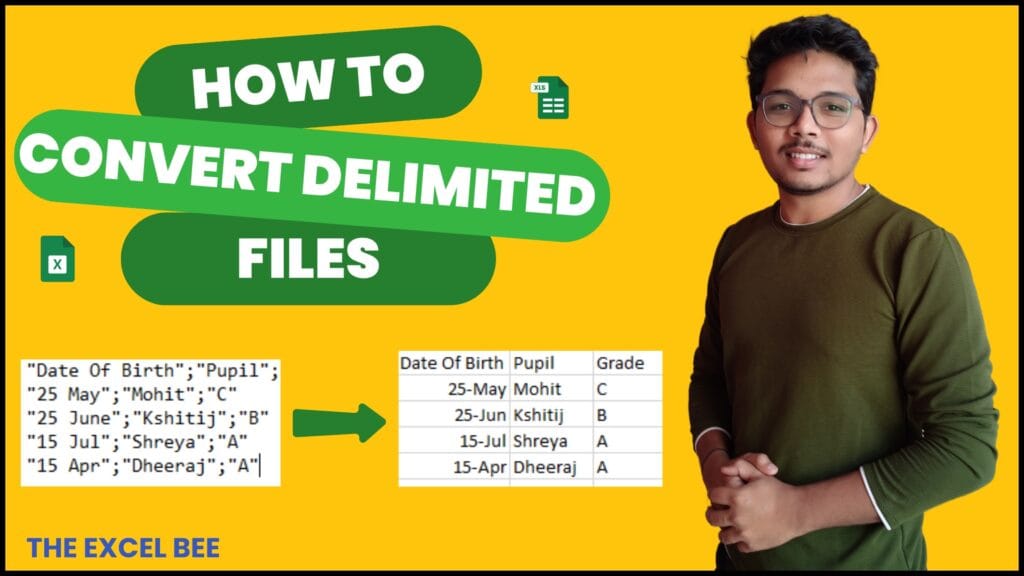
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…