What is Accounts Payable (AP)?
Accounts Payable (AP) refers to the short-term liabilities a company owes to suppliers and vendors for goods or services received on credit. It appears as a current liability on the balance sheet and represents outstanding obligations that need to be settled within a specific period. Proper AP management ensures smooth business operations and maintains good vendor relationships.
Understanding the Accounts Payable Process
Managing AP involves several crucial steps:
- Invoice Receipt – Businesses receive invoices from suppliers for goods or services provided.
- Invoice Verification – Cross-checking the invoice with purchase orders and delivery receipts to ensure accuracy.
- Approval Process – Internal approval from relevant departments before processing payments.
- Payment Processing – Issuing payments based on due dates and payment terms.
- Record Keeping – Proper documentation for audit and compliance purposes.
Efficient AP management reduces errors, prevents fraud, and optimizes cash flow.
Importance of Accounts Payable in Business
Accounts Payable plays a vital role in financial management:
- Maintains Cash Flow – Ensures a balance between incoming and outgoing cash.
- Enhances Vendor Relationships – Timely payments build trust with suppliers.
- Avoids Late Fees & Penalties – Prevents unnecessary financial burdens.
- Supports Financial Accuracy – Keeps company records up to date for financial reporting.
Best Practices for Accounts Payable Management
Implementing best practices can streamline AP operations and enhance financial efficiency:
- Automate AP Processes – Use AP software to reduce manual errors and improve efficiency.
- Implement Internal Controls – Prevent fraud with approval workflows and segregation of duties.
- Negotiate Payment Terms – Work with vendors to secure favorable payment conditions.
- Monitor AP Aging Reports – Track due invoices to avoid overdue payments.
- Reconcile Statements Regularly – Cross-check AP records with supplier statements.
Also Read : Kroger CEO Rodney McMullen Resigns Following Personal Conduct Investigation
Challenges in Accounts Payable & How to Overcome Them
Some common AP challenges include:
- Duplicate Payments & Errors – Automated systems can prevent duplication and miscalculations.
- Fraudulent Invoices – Implementing strict verification controls helps detect fraud.
- Late Payments – Setting reminders and prioritizing payments ensure timely settlements.
Accounts Payable Automation & Technology
Modern businesses leverage AP automation tools to simplify processes. Benefits of AP automation include:
- Faster processing times
- Reduced manual errors
- Improved compliance and security
- Better financial reporting and analytics
Conclusion
Accounts Payable (AP) is a crucial component of business financial management. Efficient AP processes ensure smooth cash flow, strengthen vendor relationships, and support overall financial stability. Implementing best practices and automation can optimize AP management, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency.
Would you like to explore specific AP software solutions or integration strategies? Let me know!
Also Read : Accounting Theory: Definition, Principles, and Importance
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is Accounts Payable different from Accounts Receivable?
Accounts Payable (AP) is money a company owes, while Accounts Receivable (AR) is money the company is owed.
2. Why is Accounts Payable important?
It helps manage cash flow, ensures timely payments, and maintains vendor relationships.
3. How can businesses improve their AP process?
By automating payments, setting approval workflows, reconciling statements, and tracking due dates.
4. What are the risks of poor AP management?
Late fees, cash flow problems, duplicate payments, and potential compliance issues.
5. What is AP automation?
It’s the use of software to streamline invoice processing, approvals, and payments, reducing errors and fraud.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
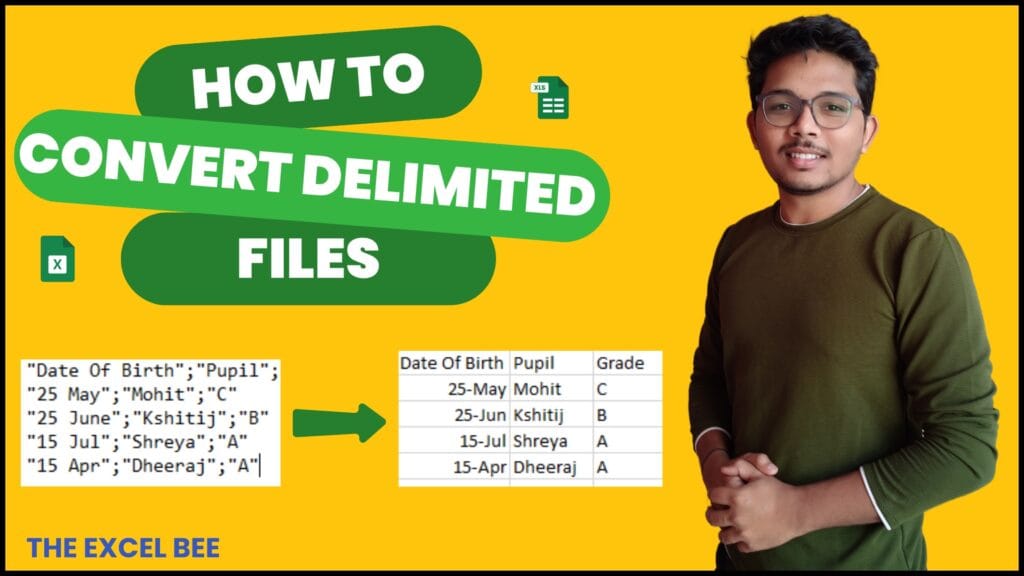
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…