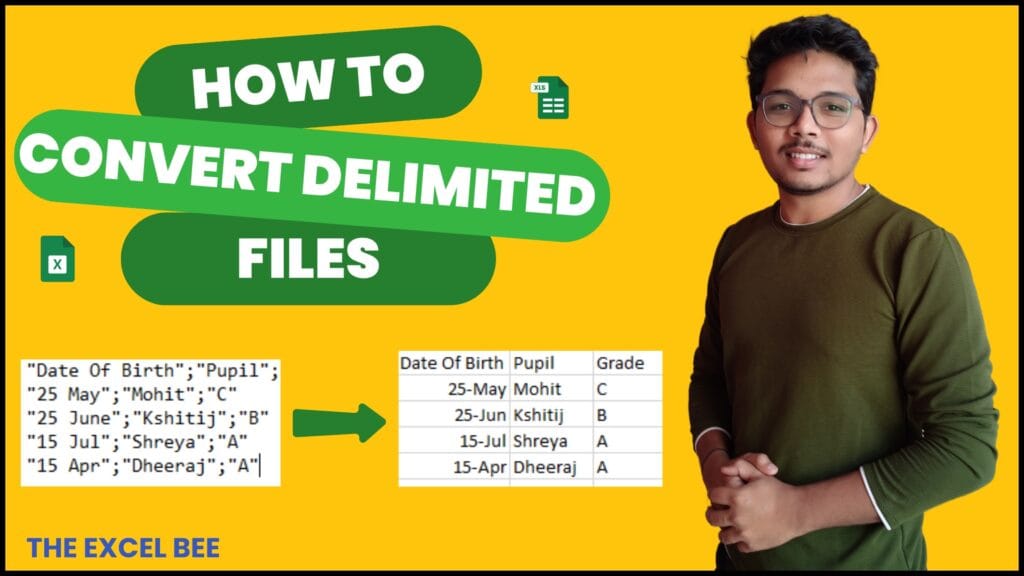
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel, the data often appears in a single column instead of being split into separate columns. Fortunately, Excel provides a simple way to convert delimited data into structured columns.
Step-by-Step Guide to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
Method 1: Using Text to Columns Feature
If your CSV data appears in a single column, follow these steps:
- Open Your CSV File in Excel
- Open Excel and go to
File > Openand select your CSV file.
- Open Excel and go to
- Select the Column Containing Data
- Click on the column (usually Column A) where the delimited data appears.
- Use the Text to Columns Wizard
- Go to the
Datatab and click onText to Columns.
- Go to the
- Choose the Delimited Option
- In the Convert Text to Columns Wizard, select
Delimitedand clickNext.
- In the Convert Text to Columns Wizard, select
- Select the Delimiter
- Choose the appropriate delimiter:
- Comma (,) if the data is separated by commas.
- Tab, Semicolon, Space, or Other if applicable.
- Click
Next.
- Choose the appropriate delimiter:
- Format the Columns (Optional)
- Choose the column data format (General, Text, or Date) based on your needs.
- Click
Finishto apply the changes.
- Review the Data
- The column will now be split into multiple columns based on the chosen delimiter.
Final Thoughts
Converting delimited CSV data into structured columns in Excel is straightforward using the Text to Columns tool, Power Query, or Excel functions. Choose the best method based on your dataset size and formatting needs.
By following these steps, you can efficiently organize your data for analysis and reporting. Happy Excel-ing!