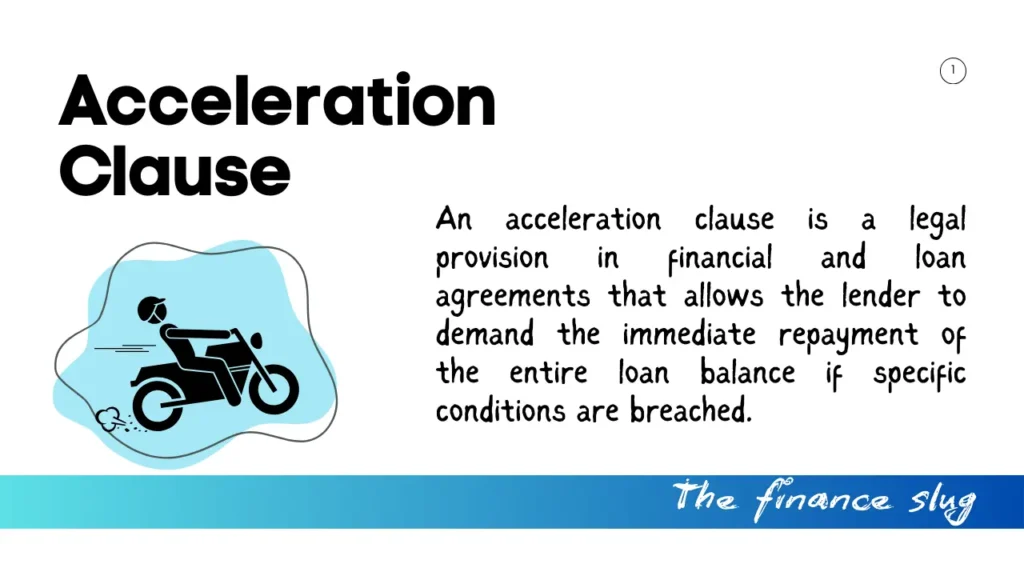
What Is an Acceleration Clause?
An acceleration clause is a legal provision in financial and loan agreements that allows the lender to demand the immediate repayment of the entire loan balance if specific conditions are breached. Typically, this clause is triggered by a borrower’s failure to meet obligations, such as missing payments or violating other contractual terms.
While acceleration clauses are designed to protect lenders, they also encourage borrowers to maintain compliance with their agreements. Understanding how they work, their implications, and how to avoid triggering them can help both borrowers and lenders navigate financial contracts with confidence.
Definition and Purpose of an Acceleration Clause
An acceleration clause is a safeguard embedded in loan contracts that empowers lenders to accelerate the repayment timeline if certain conditions are violated. Instead of following the originally agreed schedule, the borrower is required to pay the entire outstanding balance in a single lump sum.
Origins of the Acceleration Clause in Contracts
The concept of acceleration clauses emerged as a way to mitigate financial risks in long-term loan agreements. By allowing lenders to secure their funds quickly in case of borrower default, the clause has become a standard component of mortgages, commercial loans, and business contracts.
Also read: Financial Statements 101: Learn How to Read and Analyze Them
Why Acceleration Clauses Are Important in Agreements
These clauses play a dual role. For lenders, they serve as a safety net, ensuring timely repayment and reducing the risk of prolonged financial losses. For borrowers, they promote financial accountability by reinforcing the importance of meeting contract terms.
How Does an Acceleration Clause Work?
Acceleration clauses function as a trigger mechanism. When specific conditions outlined in the contract are breached, the lender gains the right to demand full repayment of the loan.
The Mechanism of Acceleration
Once triggered, the lender typically issues a formal notice to the borrower. This notice outlines the violation, explains the acceleration of the repayment schedule, and provides a timeline for payment. Borrowers are often given a chance to rectify the breach, but failure to comply can result in severe consequences, such as foreclosure or legal action.
Common Scenarios That Trigger an Acceleration Clause
- Non-payment of loan installments.
- Breach of other contract terms, such as failing to maintain insurance.
- Filing for bankruptcy or becoming insolvent.
- Sale or transfer of collateral without lender approval.
Types of Acceleration Clauses
Not all acceleration clauses are the same. They vary based on the type of financial agreement and the conditions outlined in the contract.
Mortgage Acceleration Clause
This is one of the most common forms of acceleration clauses, typically included in residential mortgage agreements. If a borrower misses payments or violates terms like maintaining home insurance, the lender can demand the full repayment of the loan balance.
Commercial Loan Acceleration Clause
In commercial agreements, acceleration clauses may activate when businesses fail to meet financial benchmarks, such as maintaining adequate revenue or adhering to loan covenants.
Business Contracts with Acceleration Provisions
In business transactions, these clauses often relate to installment payments for acquisitions or mergers. A buyer’s failure to adhere to the payment schedule can trigger immediate repayment of the outstanding balance.
Also read: What is Credit? The Key to Financial Growth and Success
Advantages of an Acceleration Clause
Acceleration clauses offer benefits, especially for lenders, but they also contribute to maintaining fairness and accountability in financial contracts.
Protecting Lenders and Creditors
These clauses are a vital tool for lenders, providing them with the ability to reclaim funds quickly in case of borrower default. This minimizes potential losses and strengthens financial stability.
Encouraging Timely Payment Compliance
For borrowers, the existence of an acceleration clause serves as a motivation to meet payment obligations on time. Knowing the serious consequences of default often encourages better financial discipline.
Disadvantages and Risks of Acceleration Clauses
While acceleration clauses are beneficial for lenders, they can create significant challenges for borrowers and carry certain risks.
Potential for Financial Strain on Borrowers
When triggered, an acceleration clause can force borrowers into an overwhelming financial situation. For example, a homeowner who has missed a few mortgage payments may suddenly be required to repay the entire remaining balance, often leading to foreclosure.
Legal Risks for Lenders and Borrowers
Poorly drafted or ambiguous acceleration clauses can lead to legal disputes. Borrowers might contest the activation of the clause, claiming it was enforced unfairly. Lenders, on the other hand, must ensure they follow proper legal procedures, such as issuing a notice, to avoid complications.
Triggers for Activating an Acceleration Clause
Understanding the triggers that activate an acceleration clause is crucial to avoid its consequences.
Non-Payment or Default Scenarios
The most common trigger for an acceleration clause is non-payment. This can include missed payments or consistent delays. Additionally, breaching other contract terms, such as failing to pay property taxes or maintain insurance, can also lead to activation.
Bankruptcy or Insolvency
Borrowers who declare bankruptcy or are deemed insolvent may activate the clause, as lenders aim to secure their funds before the borrower’s assets are distributed among creditors.
Sale or Transfer of Secured Property
If a borrower sells or transfers ownership of the property securing the loan without the lender’s approval, the clause can be triggered to protect the lender’s interests.
Legal Implications of Acceleration Clauses
Acceleration clauses come with legal obligations and rights for both lenders and borrowers.
Borrower Rights Under Acceleration Clauses
Borrowers are entitled to specific rights, such as:
- Receiving formal notice of activation.
- Challenging the activation if they believe it was improperly enforced.
- Negotiating with lenders to resolve the breach.
Lender Responsibilities and Legal Framework
Lenders must strictly adhere to the legal framework governing acceleration clauses. This includes clearly outlining the terms in the contract, issuing timely notices, and allowing borrowers an opportunity to address the issue before enforcing the clause.
Negotiating Acceleration Clauses in Contracts
When drafting or signing a financial agreement, it’s essential to carefully review and negotiate the terms of the acceleration clause.
Key Factors to Consider During Negotiation
- Clarity of Terms: Ensure that the triggers for activation are clearly defined to avoid misunderstandings.
- Reasonable Triggers: Avoid overly strict or unreasonable triggers that could unfairly penalize the borrower.
Importance of Legal Advice
Both borrowers and lenders should seek legal counsel when drafting acceleration clauses to ensure they are fair, transparent, and enforceable under applicable laws.
Examples of Acceleration Clauses in Real-World Contracts
Residential Mortgage Agreements
Homeowners who fail to meet payment schedules or other obligations, such as maintaining property insurance, may face acceleration clauses that require them to pay the full loan amount.
Business Loan Agreements
In business financing, acceleration clauses are often tied to financial performance metrics. If a business fails to meet revenue targets or breaches loan covenants, the lender can demand immediate repayment.
How to Respond to an Activated Acceleration Clause
Steps for Borrowers to Resolve Payment Issues
- Negotiate with the Lender: Open communication can often lead to alternative solutions, such as modified repayment plans.
- Seek Legal Counsel: A lawyer can help assess the validity of the activation and explore options for resolution.
Preventing Escalation Through Proactive Measures
To avoid triggering an acceleration clause, borrowers should:
- Make payments on time.
- Maintain communication with the lender if financial difficulties arise.
- Adhere to all other contractual terms, such as maintaining insurance or paying taxes.
Common Misconceptions About Acceleration Clauses
The Clause Always Favors Lenders
While acceleration clauses primarily protect lenders, they can also benefit borrowers by encouraging clear and fair terms in financial agreements.
Borrowers Have No Recourse Once Triggered
Borrowers do have options, such as negotiating with lenders or seeking legal assistance, to address or challenge the activation of the clause.
Conclusion
Acceleration clauses are a critical part of financial and loan agreements, providing lenders with a way to secure repayment while promoting accountability among borrowers. Although they can create challenges, understanding their function and implications can help parties navigate contracts effectively. By reviewing terms carefully, seeking legal advice, and maintaining proactive communication, borrowers and lenders can minimize risks and foster fair agreements.
FAQs
What is the purpose of an acceleration clause?
It ensures lenders can demand full repayment if the borrower breaches specific terms of the agreement.
Can borrowers contest an activated acceleration clause?
Yes, borrowers can challenge the clause in court or negotiate alternative solutions with the lender.
Are acceleration clauses common in all loans?
No, they are most commonly found in mortgages, commercial loans, and business agreements.
What happens if a borrower cannot pay the accelerated amount?
Borrowers may face foreclosure or legal action but can negotiate with the lender or seek legal advice for alternatives.
How can borrowers prevent triggering an acceleration clause?
By making payments on time, maintaining communication with lenders, and adhering to all contract terms.
Article Resources
- Legal information institute: https://www.law.cornell.edu/wex/acceleration_clause#:~:text=An%20acceleration%20clause%20is%20a,materially%20breaches%20a%20loan%20agreement.
- Investopedia: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/a/acceleration-clause.asp
- corporatefinanceinstitute: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/commercial-lending/acceleration-clause/
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
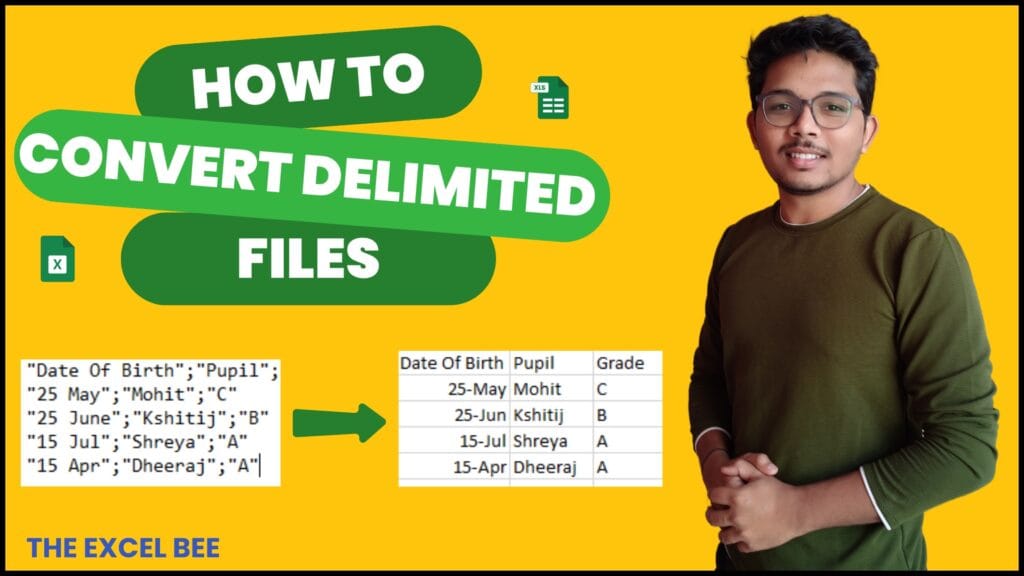
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…