- Introduction
- Key Components of an Accounting Information System
- Functions and Objectives of AIS
- Types of Accounting Information Systems
- Benefits of an Efficient AIS
- Challenges and Risks of AIS
- AIS vs. Traditional Accounting Systems
- Popular AIS Software in the Market
- AIS and Emerging Technologies
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Introduction
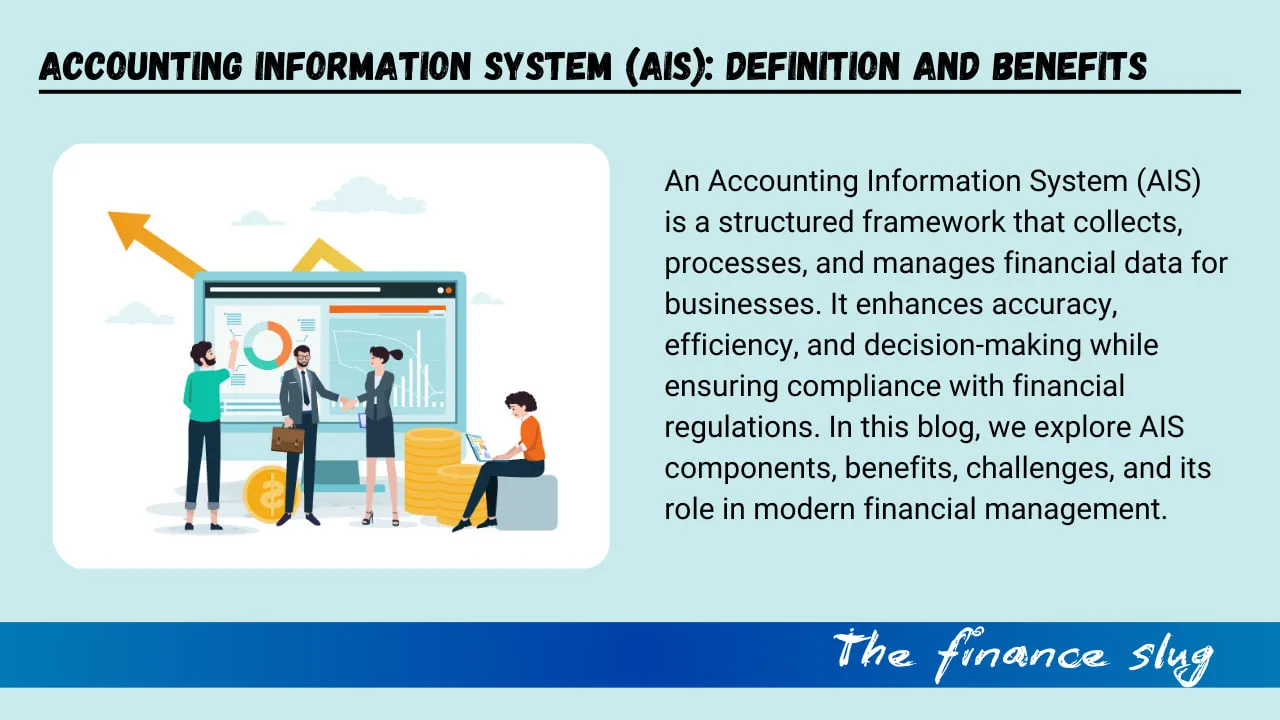
In today’s fast-paced business world, financial data management is crucial for the success of any organization. This is where an Accounting Information System (AIS) comes into play. AIS is a structured framework that collects, processes, and stores financial information, enabling businesses to make informed decisions. Whether a small startup or a multinational corporation, every organization relies on AIS to manage its financial transactions, ensure regulatory compliance, and improve overall efficiency.
With the advancement of technology, AIS has evolved from manual bookkeeping methods to sophisticated cloud-based systems that integrate with various business functions. This article explores the key components, functions, benefits, challenges, and future trends of Accounting Information Systems.
Key Components of an Accounting Information System
A well-functioning AIS consists of several critical components, each playing a vital role in the system’s effectiveness:
1. People (Users and Stakeholders)
AIS users include accountants, auditors, financial managers, business executives, and regulatory authorities. Each user interacts with the system to record transactions, analyze financial data, and generate reports for decision-making.
2. Procedures and Instructions
These define how data is collected, recorded, processed, and stored. Procedures ensure consistency and accuracy in financial reporting, reducing errors and fraud risks.
3. Data (Financial and Non-Financial)
AIS captures various data, including sales records, purchase orders, payroll information, tax filings, and other financial transactions. Accurate data input is crucial for reliable financial analysis.
4. Software (Accounting Software and ERP Systems)
Software applications like QuickBooks, SAP, and Oracle help automate accounting functions, making data management more efficient and secure. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate AIS with other business processes.
5. IT Infrastructure (Hardware and Networks)
AIS requires robust hardware, including servers, computers, and secure network connections, to ensure smooth operation and data accessibility.
6. Internal Controls and Security Measures
Security protocols, such as encryption, access controls, and audit trails, protect AIS from fraud, unauthorized access, and cyber threats.
Also Read : Accounting Equation Explained: Formula, Importance & Examples
Functions and Objectives of AIS
An effective AIS serves multiple purposes, making it an essential tool for financial management.
1. Recording Financial Transactions
AIS ensures that all financial transactions are accurately recorded, categorized, and stored for easy retrieval and auditing.
2. Processing and Storing Financial Data
The system processes transactions in real-time and securely stores historical financial data for future reference.
3. Generating Financial Reports
AIS produces financial statements, balance sheets, and income statements that help organizations assess their financial health.
4. Enhancing Decision-Making
AIS provides financial insights that aid in budgeting, forecasting, and strategic planning.
5. Ensuring Compliance and Security
With built-in compliance features, AIS ensures adherence to tax laws, financial regulations, and industry standards.
Types of Accounting Information Systems
AIS can be classified into three main types:
1. Manual AIS
Traditional bookkeeping methods involve recording transactions manually in ledgers and journals. This system is prone to errors and inefficiencies.
2. Computerized AIS
Modern AIS automates accounting functions using specialized software, improving accuracy and efficiency.
3. Cloud-Based AIS
Cloud-based solutions allow businesses to access financial data from anywhere, offering scalability, security, and real-time collaboration.
Benefits of an Efficient AIS
✅ Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
Automation reduces manual errors, ensuring reliable financial reporting.
✅ Faster and More Efficient Processing
AIS speeds up transaction processing and report generation, saving time and resources.
✅ Better Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
AIS helps businesses comply with tax regulations and financial reporting standards.
✅ Enhanced Decision-Making and Strategic Planning
AIS provides real-time financial insights that drive business growth.
✅ Increased Security and Fraud Prevention
Robust security measures protect sensitive financial data from fraud and cyber threats.
Challenges and Risks of AIS
Despite its benefits, AIS also faces challenges:
- Data Security and Cyber Threats: Businesses must safeguard against hacking and data breaches.
- System Implementation Costs: AIS setup and maintenance can be expensive.
- User Training and Adaptation Issues: Employees need training to use AIS effectively.
- Risk of System Failures and Data Loss: Regular backups and contingency plans are necessary.
AIS vs. Traditional Accounting Systems
| Feature | AIS (Computerized) | Traditional Accounting (Manual) |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Speed | Fast & Automated | Slow & Manual |
| Accuracy | High (Automated) | Prone to Errors |
| Integration | Easily Integrated | Standalone System |
| Data Security | High (Encryption & Access Control) | Low (Physical Security Risks) |
| Compliance | Automated Compliance Checks | Requires Manual Effort |
Popular AIS Software in the Market
- QuickBooks – Ideal for small businesses
- SAP ERP – Best for large enterprises
- Oracle Financials – Powerful financial management solution
- Xero – Cloud-based accounting for startups and SMEs
AIS and Emerging Technologies
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI-powered AIS improves fraud detection, predictive analytics, and automated financial processing.
2. Blockchain for Secure Transactions
Blockchain enhances financial security and ensures transparent, tamper-proof records.
3. Cloud Computing and Remote Access
Cloud-based AIS allows remote financial management, reducing hardware dependency.
Conclusion
AIS plays a crucial role in modern financial management, streamlining accounting processes and improving decision-making. With rapid technological advancements, AIS continues to evolve, integrating AI, blockchain, and cloud computing for enhanced efficiency and security. Businesses that adopt and optimize AIS can achieve greater financial accuracy, compliance, and growth.
Also Read : Accounting Cycle: Step-by-Step Guide for Accurate Financial Reporting
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main purpose of AIS?
AIS is designed to collect, process, and store financial data, enabling businesses to manage transactions, generate reports, and make informed decisions.
2. How does AIS improve financial reporting?
AIS automates data recording and reporting, reducing errors and ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
3. What are the risks of using AIS?
Common risks include cyber threats, system failures, high implementation costs, and user adaptation challenges.
4. Is cloud-based AIS better than traditional AIS?
Cloud-based AIS offers flexibility, remote access, and enhanced security compared to traditional on-premise systems.
5. Can small businesses benefit from AIS?
Yes, small businesses can use AIS to improve financial accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
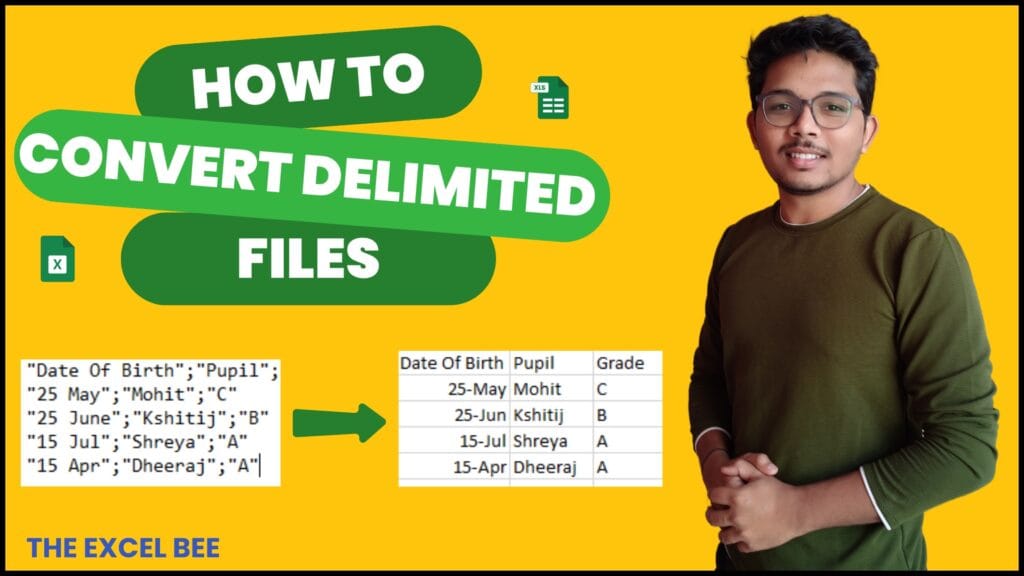
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…