- What Are Accounting Policies?
- Why Are Accounting Policies Important?
- Key Components of Accounting Policies
- Types of Accounting Policies
- Examples in Practice
- How to Choose the Right Accounting Policies
- How Accounting Policies Impact Financial Statements
- Accounting Policies vs. Accounting Estimates
- Common Accounting Policy Disclosures in Financial Reports
- Challenges in Implementing
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Are Accounting Policies?
Accounting policies are the specific principles, bases, conventions, rules, and practices applied by a company when preparing and presenting its financial statements. These policies guide how financial transactions are recorded, ensuring consistency and comparability in financial reporting.
Companies follow accounting policies that align with established accounting frameworks like Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) to maintain accuracy and transparency.
Why Are Accounting Policies Important?
1. Ensures Consistency in Financial Reporting
Accounting policies create a structured approach to recording financial transactions, enabling businesses to maintain consistency across reporting periods. This is crucial for internal decision-making and external stakeholders like investors and regulators.
2. Enhances Comparability
By following standardized accounting policies, businesses make it easier for stakeholders to compare their financial performance with industry peers. Investors and analysts rely on consistent accounting treatments to assess financial health.
3. Improves Financial Transparency
A well-defined accounting policy promotes transparency, ensuring that a company’s financial position is accurately represented. This helps build trust with investors, creditors, and regulatory authorities.
4. Compliance with Regulatory Standards
Governments and financial authorities mandate that businesses follow specific accounting policies to comply with laws and avoid penalties. Adherence to IFRS or GAAP is often a legal requirement for publicly traded companies.
Key Components of Accounting Policies
1. Recognition of Revenue and Expenses
Companies determine when to recognize revenue and expenses. This decision impacts profitability and financial statements significantly.
- Accrual Basis Accounting: Revenue is recorded when earned, not when cash is received.
- Cash Basis Accounting: Revenue is recorded only when cash is received.
2. Valuation of Assets and Liabilities
Accounting policies define how a company values assets and liabilities. Methods include:
- Historical Cost Method – Assets recorded at original purchase price.
- Fair Value Method – Assets valued based on current market conditions.
3. Depreciation and Amortization Policies
Businesses define depreciation methods for tangible assets and amortization for intangible assets. Common depreciation methods include:
- Straight-Line Depreciation – Spreads cost evenly over asset life.
- Declining Balance Method – Higher depreciation in earlier years.
4. Inventory Valuation
The method used for inventory valuation can impact financial statements. Common inventory methods include:
- FIFO (First-In, First-Out): Oldest inventory is used first.
- LIFO (Last-In, First-Out): Newest inventory is used first.
- Weighted Average Cost: Inventory cost is averaged over time.
Types of Accounting Policies
1. Conservative vs. Aggressive
- Conservative Accounting: Focuses on minimizing risks by recognizing expenses earlier and revenue later.
- Aggressive Accounting: Aims to show higher profits by recognizing revenue sooner and deferring expenses.
2. Mandatory vs. Voluntary
- Mandatory Policies: Required by law (e.g., IFRS/GAAP compliance).
- Voluntary Policies: Chosen by companies to improve reporting efficiency.
Examples in Practice
- Tech Companies (e.g., Apple, Google): Follow accrual-based accounting and IFRS standards for revenue recognition.
- Retail Industry (e.g., Walmart, Amazon): Use FIFO or weighted average cost for inventory valuation.
- Manufacturing Firms: Implement depreciation policies for large-scale equipment and machinery.
Also Read : What is an Accounting Method? Types, Examples, and Best Practices
How to Choose the Right Accounting Policies
- Align with Regulatory Standards: Ensure compliance with IFRS, GAAP, or local accounting standards.
- Consider Industry Practices: Adopt policies that align with best practices in your sector.
- Maintain Consistency: Avoid frequent changes to maintain comparability.
- Disclose Policies Clearly: Clearly state accounting policies in financial reports for transparency.
How Accounting Policies Impact Financial Statements
Balance Sheet Impact
Different policies affect asset and liability valuation, influencing overall financial position.
Income Statement Impact
Revenue recognition policies determine reported earnings, affecting investor decisions.
Cash Flow Statement Impact
Depreciation and inventory valuation policies influence reported cash flow.
Accounting Policies vs. Accounting Estimates
| Feature | Accounting Policies | Accounting Estimates |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of principles and methods | Adjustments based on new information |
| Example | Revenue recognition methods | Bad debt provisions |
| Changeability | Usually stable over time | Adjusted when new data arises |
Common Accounting Policy Disclosures in Financial Reports
Companies disclose accounting policies in their financial statements, usually in the Notes to Financial Statements section. Key disclosures include:
- Revenue Recognition Policy
- Depreciation & Amortization Methods
- Inventory Valuation Method
- Foreign Currency Translation Policies
Challenges in Implementing
- Frequent Regulatory Changes: IFRS and GAAP updates require companies to adapt continuously.
- Complexity in Application: Some policies are difficult to implement, especially in multinational firms.
- Potential Manipulation: Companies may exploit policies to manipulate earnings.
Final Thoughts
Accounting policies play a crucial role in ensuring accurate, consistent, and transparent financial reporting. Whether you’re an investor, accountant, or business owner, understanding these policies can help you make better financial decisions. Companies must adhere to established accounting standards, disclose their policies transparently, and apply them consistently to maintain credibility in financial markets.
Also Read : Accounting Information System (AIS): Definition, Components, and Benefits
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can a company change its accounting policies?
Yes, but only if the new policy improves financial reporting or is required due to regulatory changes. Such changes must be disclosed in financial reports.
2. How do accounting policies affect tax reporting?
Different policies impact taxable income and, consequently, the amount of tax a company pays. Depreciation methods and inventory valuation play a significant role.
3. Are accounting policies the same across all industries?
No, different industries may follow varying policies based on their business models and regulatory requirements.
4. Where can I find a company’s accounting policies?
You can find a company’s accounting policies in the Notes to Financial Statements section of their annual report or financial filings.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
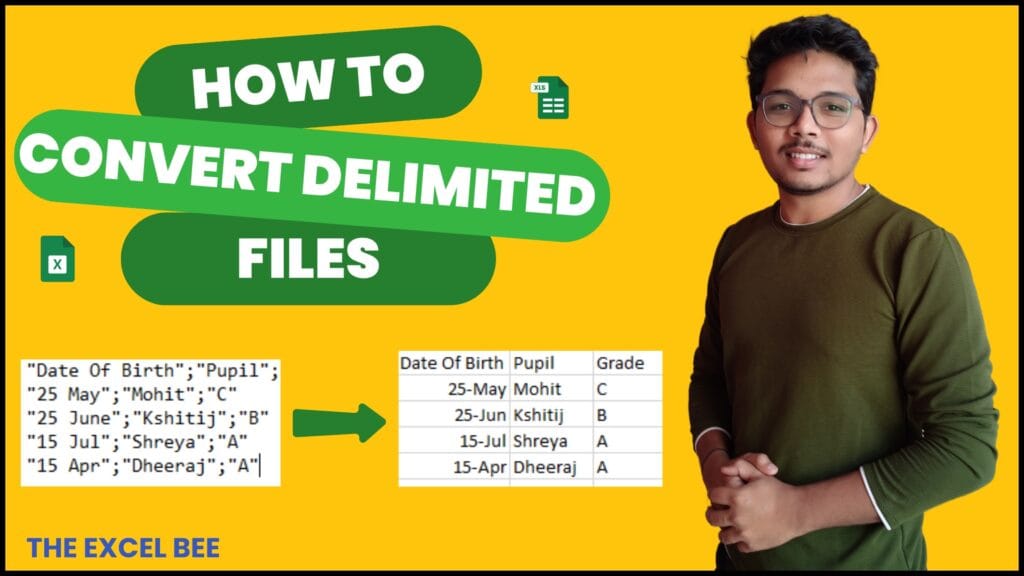
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…