Introduction
Accounting profit is a fundamental financial metric that helps businesses and investors assess profitability. It represents the net income a company earns after deducting explicit costs from total revenue. Understanding accounting profit is essential for financial reporting, taxation, and business decision-making.
This guide will explore the concept of accounting profit in detail, including its formula, calculation, importance, and differences from economic profit. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of why accounting profit matters and how businesses use it to measure financial success.
What Is Accounting Profit?
Accounting profit is the profit a company reports on its financial statements. It is calculated as:Accounting Profit=Total Revenue−Explicit Costs\text{Accounting Profit} = \text{Total Revenue} – \text{Explicit Costs}Accounting Profit=Total Revenue−Explicit Costs
- Total Revenue: The total income generated from sales of goods or services.
- Explicit Costs: These include all direct, out-of-pocket expenses like wages, rent, materials, and utilities.
Accounting profit does not account for implicit costs (opportunity costs), making it different from economic profit.
How to Calculate Accounting Profit?
To calculate accounting profit, follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify Total Revenue
Determine the company’s total revenue from all business operations.
Step 2: List Explicit Costs
Include expenses such as:
- Employee salaries and wages
- Rent or lease payments
- Raw materials and supplies
- Utility bills
- Depreciation of assets
- Interest on loans
- Taxes
Step 3: Subtract Explicit Costs from Revenue
Accounting Profit=Total Revenue−Explicit Costs\text{Accounting Profit} = \text{Total Revenue} – \text{Explicit Costs}Accounting Profit=Total Revenue−Explicit Costs
Example Calculation
Let’s assume:
- Total Revenue = $500,000
- Explicit Costs = $350,000
Accounting Profit=500,000−350,000=150,000\text{Accounting Profit} = 500,000 – 350,000 = 150,000Accounting Profit=500,000−350,000=150,000
Thus, the company’s accounting profit is $150,000.
Also Read : What Are Accounting Principles? A Comprehensive Guide
Importance of Accounting Profit
1. Financial Performance Measurement
Accounting profit helps businesses track their profitability over time. It is a key indicator of financial health.
2. Taxation Purposes
Governments use accounting profit to assess tax liabilities. Higher profits typically mean higher taxes.
3. Investor Confidence
Investors rely on accounting profit to evaluate a company’s potential for growth and return on investment (ROI).
4. Decision-Making Tool
Business owners and managers use accounting profit to make financial and operational decisions.
5. Loan and Credit Approval
Banks and financial institutions review accounting profit before approving business loans and credit lines.
Accounting Profit vs. Economic Profit
Key Differences
| Factor | Accounting Profit | Economic Profit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Net income after deducting explicit costs | Net income after deducting explicit and implicit costs |
| Costs Considered | Only explicit costs (wages, rent, etc.) | Explicit and implicit costs (opportunity costs) |
| Calculation | Revenue – Explicit Costs | Revenue – (Explicit + Implicit Costs) |
| Usage | Used for financial reporting and taxation | Used for economic analysis and decision-making |
Example Comparison
- Accounting Profit: A company earns $200,000 in revenue and incurs $120,000 in explicit costs. Accounting profit = $80,000.
- Economic Profit: If the owner could have earned $30,000 working elsewhere (implicit cost), economic profit = $80,000 – $30,000 = $50,000.
Accounting profit always tends to be higher than economic profit because it doesn’t include opportunity costs.
Limitations of Accounting Profit
While accounting profit is useful, it has limitations:
- Ignores Opportunity Costs
- Doesn’t consider alternative income sources.
- Doesn’t Reflect True Profitability
- Economic profit provides a more comprehensive view.
- Can Be Manipulated
- Companies can adjust expenses to show higher or lower profits.
- Not Always a Good Measure for Long-Term Decisions
- Businesses focusing only on accounting profit may miss growth opportunities.
How to Improve Accounting Profit?
Companies can increase accounting profit by:
1. Increasing Revenue
- Expanding product or service offerings
- Enhancing marketing efforts
- Improving customer retention
2. Reducing Explicit Costs
- Negotiating better deals with suppliers
- Reducing operational waste
- Implementing cost-effective technology
3. Managing Expenses Efficiently
- Controlling administrative costs
- Streamlining production processes
- Reducing interest payments by refinancing debts
Conclusion
Accounting profit is a crucial financial metric that reflects a company’s profitability. It is widely used for financial reporting, taxation, and decision-making. However, it does not consider implicit costs, making economic profit a more accurate measure of overall profitability.
Understanding the differences between accounting profit and economic profit can help businesses make better financial decisions. By increasing revenue, managing expenses, and reducing costs, companies can maximize their accounting profit and improve financial stability.
Also Read : Accounting Policies: Definition, Importance & Key Examples
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between accounting profit and net profit?
Accounting profit and net profit are the same in most cases, as both refer to the profit after deducting explicit costs from total revenue.
2. Is accounting profit taxable?
Yes, businesses pay taxes based on their accounting profit after considering allowable deductions.
3. Can a company have accounting profit but negative economic profit?
Yes, if implicit costs (opportunity costs) exceed accounting profit, economic profit can be negative.
4. Why is accounting profit important for businesses?
It helps businesses track profitability, file taxes, attract investors, and secure loans.
5. How can a company increase its accounting profit?
By increasing revenue, cutting expenses, and improving operational efficiency.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
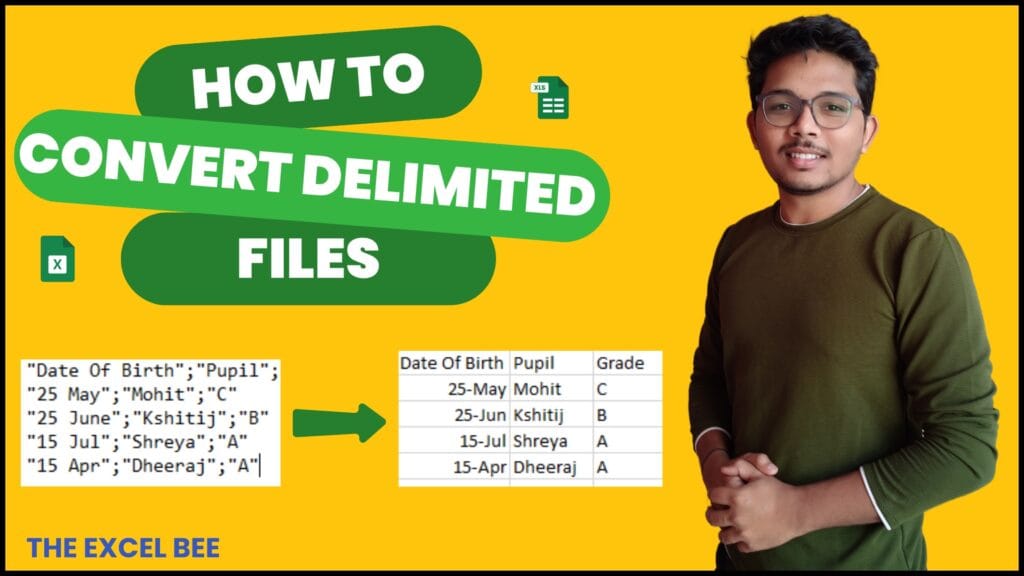
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…