In our daily lives, whether we are borrowing money, saving for retirement, or earning benefits at work, we often come across the term accrual rate. It’s a concept that sounds technical but is easy to understand when broken down. This guide will help you learn what the accrual rate means, how it works in various situations, and why it’s essential for managing your finances effectively.
What Does Accrual Rate Mean?
The accrual rate is the rate at which something grows or accumulates over time. It could be interest on a loan, money saved for retirement, or even vacation days you earn at work.
For example, if you take a loan, the accrual rate determines how quickly the interest adds up on the amount you borrowed. In a pension plan, it shows how much retirement money you earn for every year you work. In essence, it’s the building block for understanding how things increase over time in financial terms.
The accrual rate is typically expressed as a percentage or a fixed amount per period (like per month or year). Knowing this rate can help you plan better and avoid surprises.
How is Accrual Rate Used?
The accrual rate plays an important role in many aspects of life. Let’s explore some common examples:
1. Loans and Interest
When you borrow money, such as taking out a personal loan or using a credit card, the interest you pay grows based on the accrual rate.
For instance, if your loan has an annual interest rate of 12%, the monthly accrual rate would be 1% (12% divided by 12 months). This means 1% interest will be added to your outstanding loan balance every month. Understanding this can help you calculate how much you’ll owe over time and manage your payments wisely.
2. Pension and Retirement Plans
The accrual rate in retirement plans determines how much of your pension benefit you earn for each year of work.
Imagine a pension plan where the accrual rate is 2% per year. If you work for 25 years, you would earn 50% (2% × 25 years) of your final salary as your pension. So, if your final salary is $60,000, your annual pension would be $30,000. This shows why understanding the accrual rate is critical for retirement planning—it directly affects how much income you’ll have later in life.
3. Employee Benefits
Accrual rates are also used to calculate benefits like vacation or sick leave. For example, if your employer gives you 15 vacation days per year, you earn about 1.25 days each month.
This gradual build-up ensures that you earn your benefits over time. Keeping track of your accruals can help you plan your time off effectively without worrying about exceeding your entitlement.
Why is the Accrual Rate Important?
1. It Helps You Plan Ahead
The accrual rate is essential for forecasting your finances. Whether you’re calculating interest on a loan or estimating your retirement savings, knowing how things add up over time helps you make better decisions.
2. It Provides Transparency
Understanding the accrual rate means there are no surprises. You’ll know exactly how much interest you’re paying, how much pension you’re earning, or how many benefits you’re accumulating.
3. It Allows You to Compare Options
If you’re deciding between two loans or retirement plans, the accrual rate lets you compare them side-by-side. For example, a lower accrual rate on a loan means lower interest, while a higher rate in a pension plan could mean more retirement income.
Real-Life Examples of Accrual Rate
To make the concept clearer, here are a couple of real-world examples:
- Loan Example: If you take a $10,000 loan at a 12% annual interest rate and the monthly accrual rate is 1%, then at the end of the first month, $100 (1% of $10,000) in interest will be added to your loan balance.
- Retirement Example: A 35-year-old earning a $50,000 salary joins a pension plan with a 1.5% accrual rate. After 20 years of service, they would have earned a pension equal to 30% (1.5% × 20) of their salary, or $15,000 annually.
How is the Accrual Rate Calculated?
For Loans and Interest
The accrual rate for loans is calculated using the formula:
Accrual Rate=Annual Interest Rate/Number of Periods in a Year.
For example, if the annual interest rate is 12% and it’s compounded monthly, the monthly accrual rate would be: 12%÷12=1% per month.
For Pension Plans
To calculate the pension benefit:
Pension Benefit=Accrual Rate×Years of Service×Final Salary.
Here is PTO Accural rate Calculator for calculating Rate
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Confusing Accrual and Interest Rates
Some people think the accrual rate and interest rate are the same, but they’re not. The interest rate is the total percentage charged or earned annually, while the accrual rate is how much of that total applies per period (like per month).
2. Ignoring Compounding Effects
Loans and investments that use compounding can grow faster than you expect. Always consider how compounding interacts with the accrual rate.
Tools to Simplify Accrual Calculations
Technology makes managing accrual rates easier. Many financial apps and online tools allow you to calculate accruals for loans, pensions, or savings. These tools help you see the long-term effects of your financial decisions quickly and accurately.
Conclusion: Why You Should Care About the Accrual Rate
The accrual rate is more than just a financial term—it’s a key to understanding how money works over time. Whether you’re paying off a loan, saving for retirement, or earning benefits at work, knowing your accrual rate helps you stay in control of your finances.
Take a moment to check your loan statements, pension plans, or employee benefits to see how accrual rates are affecting your financial future. With this knowledge, you can make better decisions and set yourself up for success.
Have questions about how accrual rates work in your life? Share them in the comments—we’re here to help!
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
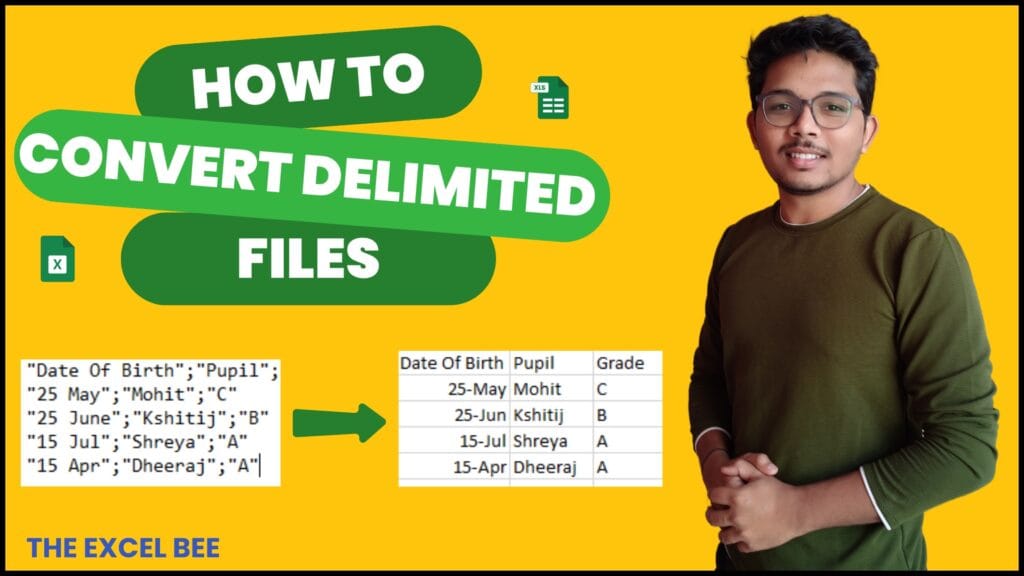
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…






Pingback: What is Accrue? History, Types, and How It Works