- Introduction
- What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
- Why Are Countries Exploring CBDCs?
- How Does CBDC Work?
- Benefits of CBDC
- Challenges and Risks of CBDC
- CBDC vs Cryptocurrency: Key Differences
- Which Countries Are Developing CBDCs?
- Future of CBDC: What Lies Ahead?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Introduction
The world of money is changing fast, and one of the biggest innovations in the financial system is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC). Governments and central banks worldwide are exploring this new form of digital money to enhance financial security, efficiency, and accessibility. But what exactly is CBDC, and why is it so important?
In this article, we’ll dive deep into what CBDC is, how it works, its advantages and risks, and how it differs from cryptocurrencies.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
CBDC is a digital version of a country’s national currency issued and controlled by the central bank. Unlike traditional cash or bank deposits, CBDC exists only in digital form but is fully backed by the central bank, ensuring stability and trust.
Key Features of CBDC:
- Issued by Central Banks – Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, CBDCs are backed by national governments.
- Digital Only – Unlike physical cash, it exists solely in electronic form.
- Stable Value – CBDCs are tied to the national currency to maintain stability.
- Secure Transactions – Uses advanced technology for secure and efficient transactions.
Why Are Countries Exploring CBDCs?
Governments and central banks are interested in CBDCs for several reasons:
- Declining Use of Cash – As digital payments become more common, fewer people use physical cash.
- Financial Inclusion – CBDCs can help unbanked populations access financial services.
- Faster and Cheaper Transactions – Digital currencies can reduce transaction costs and speed up payments.
- Control Over Monetary Policy – Unlike private cryptocurrencies, CBDCs allow governments to regulate and control money supply effectively.
- Combat Illicit Activities – CBDCs can help prevent fraud, money laundering, and illegal financial activities.
How Does CBDC Work?
CBDC works similarly to digital wallets or online banking, but with direct backing from the central bank. There are two main types of CBDCs:
1. Retail CBDC (For General Public)
- Designed for everyday use by individuals and businesses.
- Functions like digital cash for payments, transfers, and online transactions.
- Can be stored in digital wallets or linked to bank accounts.
2. Wholesale CBDC (For Banks and Financial Institutions)
- Used for transactions between banks and large institutions.
- Helps improve interbank settlements and reduce transaction costs.
- Enhances security and efficiency in financial systems.
Technology Behind CBDC
CBDCs can be built on different digital infrastructures, such as:
- Blockchain or Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) – Used to increase security and transparency.
- Centralized Digital Ledgers – Managed directly by central banks.
- Hybrid Models – Combining blockchain with centralized control for better efficiency.
Benefits of CBDC
CBDCs offer multiple advantages for individuals, businesses, and governments:
1. Financial Inclusion
- Helps people without bank accounts access digital money.
- Can be used in rural areas where banking services are limited.
2. Faster and Cheaper Transactions
- Reduces transaction costs for businesses and consumers.
- Enables real-time cross-border payments, reducing delays.
3. Enhanced Security and Transparency
- Reduces fraud, money laundering, and counterfeit risks.
- Provides better tracking and monitoring of financial transactions.
4. Supports Monetary Policies
- Gives central banks better control over inflation and interest rates.
- Enables direct government stimulus without relying on commercial banks.
5. Reduced Dependence on Cash
- Saves costs related to printing and managing physical money.
- Makes transactions more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Challenges and Risks of CBDC
Despite its benefits, CBDC also poses several challenges and risks:
1. Privacy Concerns
- Governments could track financial transactions, raising privacy issues.
- Some fear it may lead to financial surveillance.
2. Cybersecurity Risks
- Digital systems are vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks.
- A security breach could impact the entire financial system.
3. Impact on Banks
- If people switch to CBDC, commercial banks may lose deposits.
- Could affect lending and interest rates.
4. Technical and Infrastructure Challenges
- Requires significant investment in technology and digital security.
- Developing countries may face challenges in adopting CBDCs.
5. Public Trust and Acceptance
- Some people may hesitate to use CBDCs due to lack of awareness.
- Trust in government policies and regulations is crucial for success.
CBDC vs Cryptocurrency: Key Differences
| Feature | CBDC | Cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin) |
|---|---|---|
| Issuer | Central Bank | Decentralized, No central authority |
| Value Stability | Stable, tied to national currency | Highly volatile |
| Legal Status | Recognized by governments | Mostly unregulated |
| Transaction Privacy | Can be monitored by authorities | Anonymous/Pseudonymous |
| Purpose | Improve financial system | Alternative to traditional money |
While both CBDCs and cryptocurrencies exist in digital form, CBDCs are centralized and controlled by governments, whereas cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks like blockchain.
Which Countries Are Developing CBDCs?
Many nations are actively researching or launching CBDCs:
- China: Launched a pilot for the Digital Yuan (e-CNY).
- European Union: Developing the Digital Euro.
- United States: Exploring a potential Digital Dollar.
- India: Testing the Digital Rupee.
- Bahamas: First country to launch a CBDC, called the Sand Dollar.
Over 100 countries are currently studying or developing their own CBDCs, showing the growing importance of digital currencies.
Future of CBDC: What Lies Ahead?
The future of CBDCs depends on government policies, technology advancements, and public acceptance. Key developments may include:
- Wider adoption across countries.
- Better security measures to prevent cyber threats.
- Integration with existing financial systems for seamless transactions.
- New regulations to balance privacy and security.
As digital payments become the norm, CBDCs could revolutionize the global financial system, making transactions more efficient and inclusive.
Conclusion
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are shaping the future of money. They offer benefits like faster transactions, financial inclusion, and better control over monetary policies. However, they also pose challenges, including privacy risks and cybersecurity concerns.
As governments worldwide explore CBDCs, the financial world is preparing for a new era of digital money. Whether CBDCs will completely replace cash or exist alongside traditional money remains to be seen, but one thing is certain: the way we use money is changing forever.
Also Read : Accounts Receivable Financing: What It Is & How It Works
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is CBDC the same as cryptocurrency?
No, CBDC is issued by central banks and has a stable value, whereas cryptocurrencies are decentralized and highly volatile.
2. Can CBDC replace cash completely?
Not immediately, but it may reduce the use of physical cash over time.
3. Will CBDC be safe from hacking?
CBDCs will use advanced security measures, but like all digital systems, they may still face cyber threats.
4. Do I need a bank account to use CBDC?
Not necessarily; some CBDC models allow users to access digital money without a traditional bank account.
5. When will CBDCs become widely available?
Many countries are still testing CBDCs, and widespread adoption may take several years.
Stock Market Crash Today: A Bloodbath on Monday – What You Need to Know
Published on financeslug.xyz The global financial markets are reeling from a massive sell-off, and Indian…
Wall Street Bonuses Reach Record $47.5 Billion in 2024, Up 34% from Previous Year
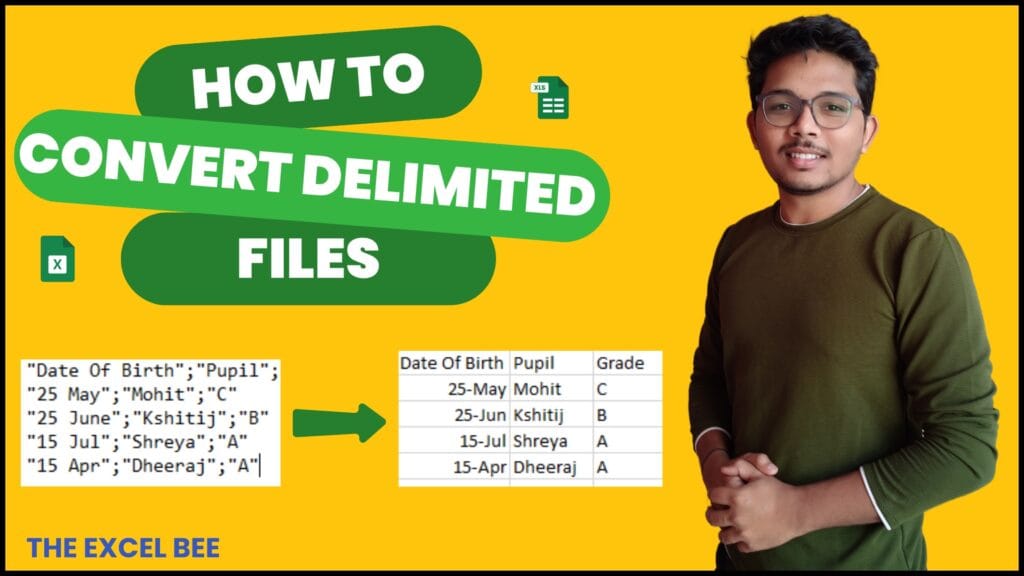
How to Convert Delimited CSV Data into Columns in Excel
CSV (Comma-Separated Values) files are widely used for data exchange, but when opened in Excel,…
Harvard University Announces Free Tuition for Families Earning $200K or Less
Harvard’s New Tuition-Free Policy: What You Need to Know Harvard University has unveiled a groundbreaking…
Eli Lilly’s 1.8B Dollar Investment in Weight Loss Drugs
Ireland’s Weight-Loss Drug Boom: A Game-Changer for Economy and Healthcare Ireland is witnessing a surge…
Forever 21 Files for Bankruptcy Again: The End of an Era in Fast Fashion?
Forever 21, once a staple in American malls and a leader in the fast-fashion industry,…